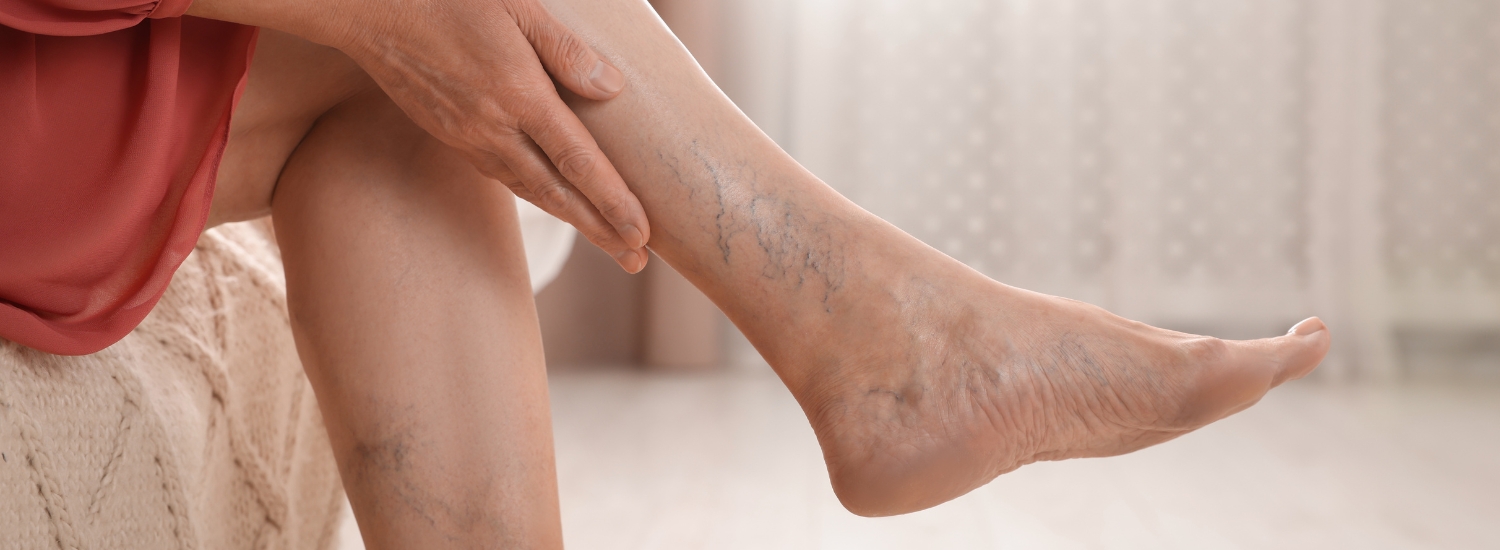
Varicose veins are swollen, twisted veins that often appear on the legs and feet. They are a common condition that affects many people, especially as they age. While varicose veins are generally not a serious health threat, they can cause discomfort and lead to more severe complications if left untreated. At Bryan Family Practice, we offer a range of vein treatment options to address varicose veins, helping you improve both your comfort and the appearance of your legs.
Table of Contents:
- What Are Varicose Veins?
- Symptoms and Complications
- Causes and Risk Factors
- Treatment Options for Varicose Veins
- When to Seek Treatment
- Final Thoughts
What Are Varicose Veins?
Varicose veins are veins that have become enlarged and twisted. They occur when the valves inside the veins weaken or become damaged, allowing blood to pool in the veins and cause them to enlarge. These veins can be blue, purple, or flesh-colored and often appear bulging or twisted on the surface of the skin.
Symptoms and Complications
Common symptoms of varicose veins include:
- Visible bulging veins, often dark blue or purple
- Swelling in the legs or ankles
- Aching or heavy feeling in the legs
- Pain or cramping in the legs
- Itching or irritation around the veins
- Skin discoloration or ulcers near the veins
If left untreated, varicose veins can lead to more serious complications, such as:
- Blood clots: Varicose veins can increase the risk of blood clot formation.
- Ulcers: Severe cases can lead to skin ulcers near the varicose veins.
- Bleeding: The veins can burst, leading to significant bleeding.
- Chronic venous insufficiency: The veins may no longer be able to adequately pump blood back to the heart, leading to swelling and pain.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of varicose veins is not fully understood, but several factors may contribute:
- Age: The risk increases with age as veins lose elasticity and the valves weaken.
- Gender: Women are more likely to develop varicose veins due to hormonal changes during pregnancy, menopause, or the use of birth control.
- Family history: A genetic predisposition can increase the likelihood of developing varicose veins.
- Pregnancy: Increased blood volume and pressure on the veins during pregnancy can lead to varicose veins.
- Obesity: Excess weight puts added pressure on the veins.
- Prolonged standing or sitting: Occupations or activities that require standing or sitting for long periods can increase the risk.
Treatment Options for Varicose Veins
There are various treatment options for varicose veins, ranging from lifestyle changes to minimally invasive procedures. Some of the most common treatments include:
1. Lifestyle Changes
- Exercise: Regular physical activity, such as walking or swimming, can help improve circulation and reduce symptoms.
- Elevating the legs: Raising the legs above the heart level can reduce swelling and discomfort.
- Compression stockings: Wearing compression stockings helps improve blood flow and reduce swelling by applying gentle pressure to the veins.
2. Sclerotherapy
Sclerotherapy is a non-surgical treatment that involves injecting a solution into the varicose vein, causing it to collapse and fade over time. This is typically used for smaller veins and is effective in improving the appearance and symptoms of varicose veins.
3. Endovenous Laser Treatment (EVLT)
Endovenous laser treatment uses laser energy to close off damaged veins. The procedure is minimally invasive and is often used for larger varicose veins. It involves inserting a thin laser fiber into the vein through a small incision.
4. Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA)
Radiofrequency ablation uses heat generated by radiofrequency energy to close off problematic veins. This procedure is similar to EVLT but uses a different method to heat the vein walls, leading to vein closure.
5. Vein Stripping and Ligation
In more severe cases, vein stripping and ligation may be necessary. This surgical procedure involves removing the affected vein through small incisions. It is typically used for large, symptomatic veins and may require general anesthesia.
6. Ambulatory Phlebectomy
This minimally invasive procedure involves removing small varicose veins through tiny punctures in the skin. It is typically used for smaller veins that are close to the surface.
7. Microphlebectomy
This procedure is similar to ambulatory phlebectomy but is used for very small veins. It can be performed under local anesthesia and is effective for removing smaller varicose veins.
When to Seek Treatment
While varicose veins may not always require medical treatment, it’s important to seek treatment if:
- You experience significant pain, swelling, or discomfort
- Your veins bleed or develop ulcers
- You experience skin changes or discoloration
- The veins are interfering with daily activities or quality of life
- You have a history of blood clots or other complications
Final Thoughts
Varicose veins are a common condition, but they can often be managed effectively with the right treatment. Whether you need lifestyle changes, non-invasive treatments, or surgery, there are various options available to help you improve the appearance and comfort of your legs. If you’re experiencing symptoms of varicose veins or are concerned about your vein health, schedule an appointment with a healthcare provider at Bryan Family Practice to discuss your treatment options.
Disclaimer: This blog is for informational purposes only and does not substitute professional medical advice. Consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment. In case of an emergency, call 911 immediately.